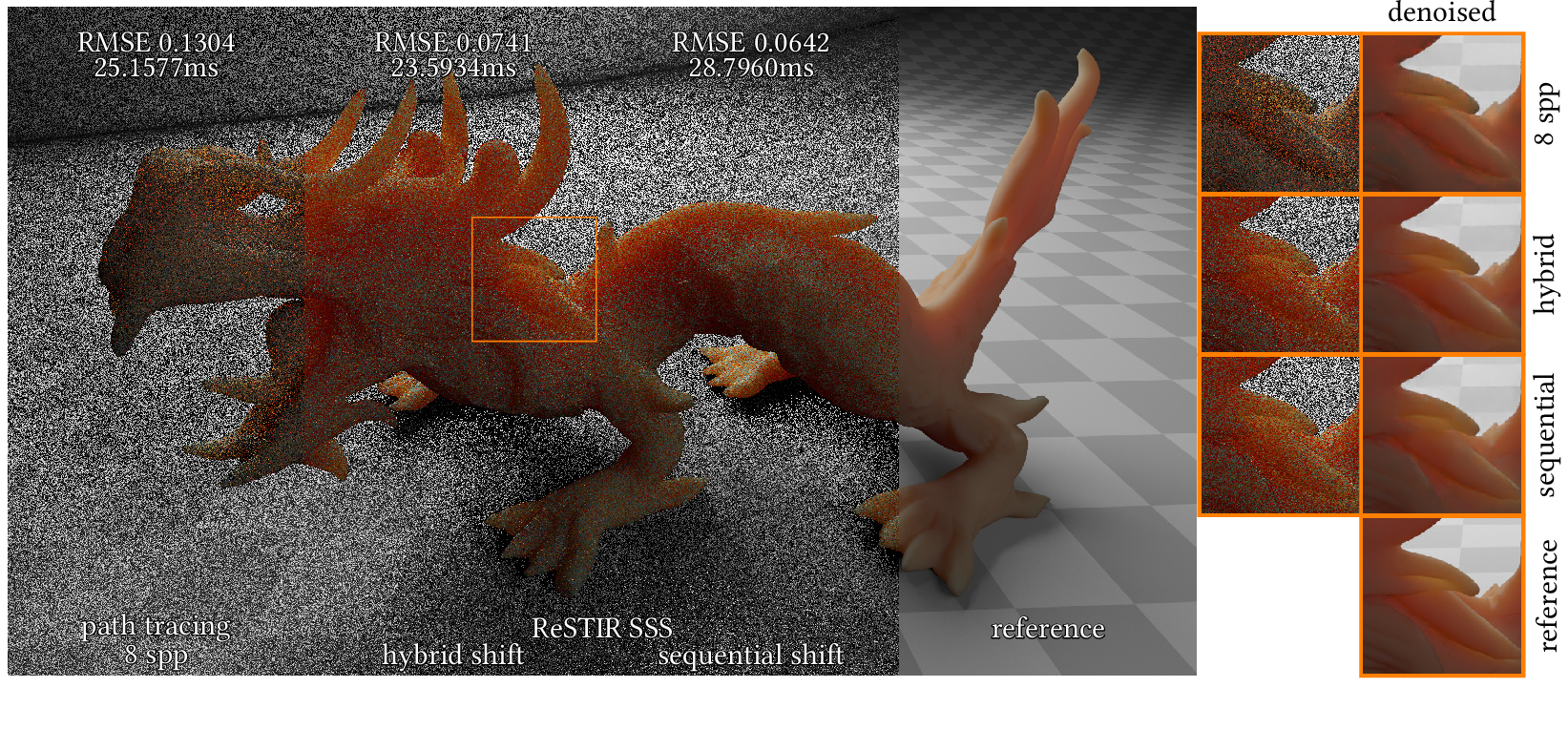
Abstract
Subsurface scattering is an important visual cue and in real-time rendering it is often approximated using
screen-space algorithms. Path tracing with the diffusion approximation can easily overcome the limitations
of these algorithms, but increases image noise. We improve its efficiency by applying reservoir-based
spatio-temporal importance resampling (ReSTIR) to subsurface light transport paths. For this, we adopt
BSSRDF importance sampling for generating candidates. Further, spatiotemporal reuse requires shifting paths
between domains. We observe that different image regions benefit most from either reconnecting through the
translucent object (reconnection shift), or one vertex later (delayed reconnection shift). We first
introduce a local subsurface scattering specific criterion for a hybrid shift that deterministically selects
one of the two shifts for a path. Due to the locality, it cannot always choose the most efficient shift,
e.g. near shadow boundaries. Therefore, we additionally propose a novel sequential shift to combine multiple
shift mappings: We execute subsequent resampling passes, each one using a different shift, which does not
require to deterministically choose a shift for a path. Instead, resampling can pick the most successful
shift implicitly. Our method achieves real-time performance and significantly reduces noise and denoising
artifacts in regions with visible subsurface scattering compared to standard path tracing with equal render
time.
Downloads
Bibtex
@article{2024_restir_sss,
author = {Mirco Werner and Vincent Schüßler and Carsten Dachsbacher},
title = {{ReSTIR Subsurface Scattering for Real-Time Path Tracing}},
journal = {Proceedings of the ACM on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (Proceedings of High Performance Graphics)},
volume = 7,
number = 3,
year = 2024,
doi = {10.1145/3675372}
}