Accepted to IEEE SciVis 2019. To appear in IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
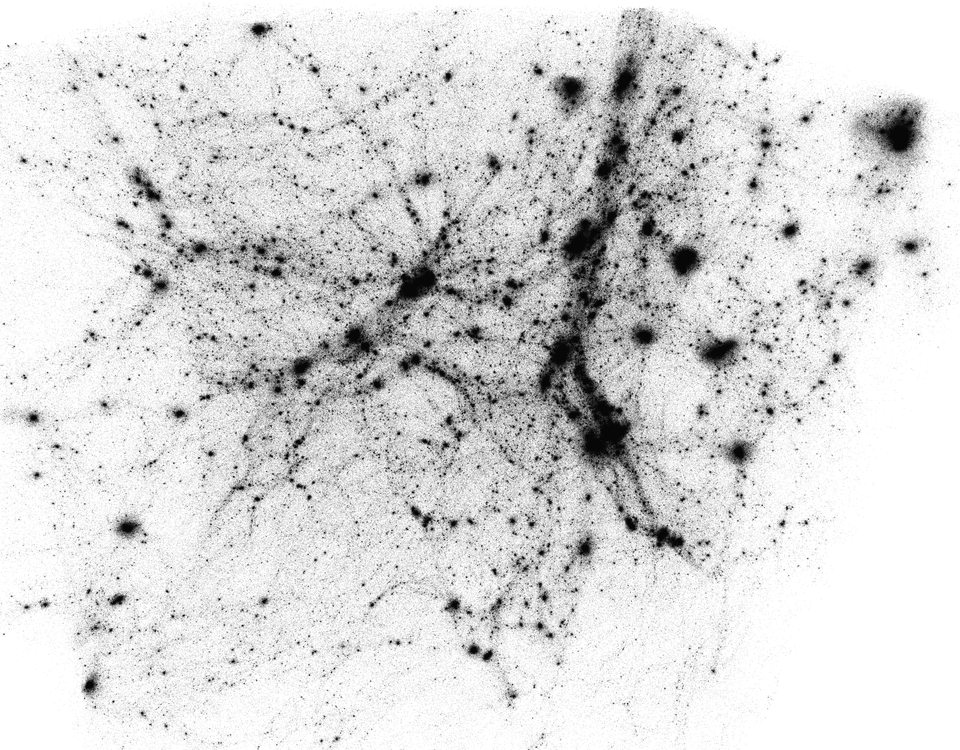
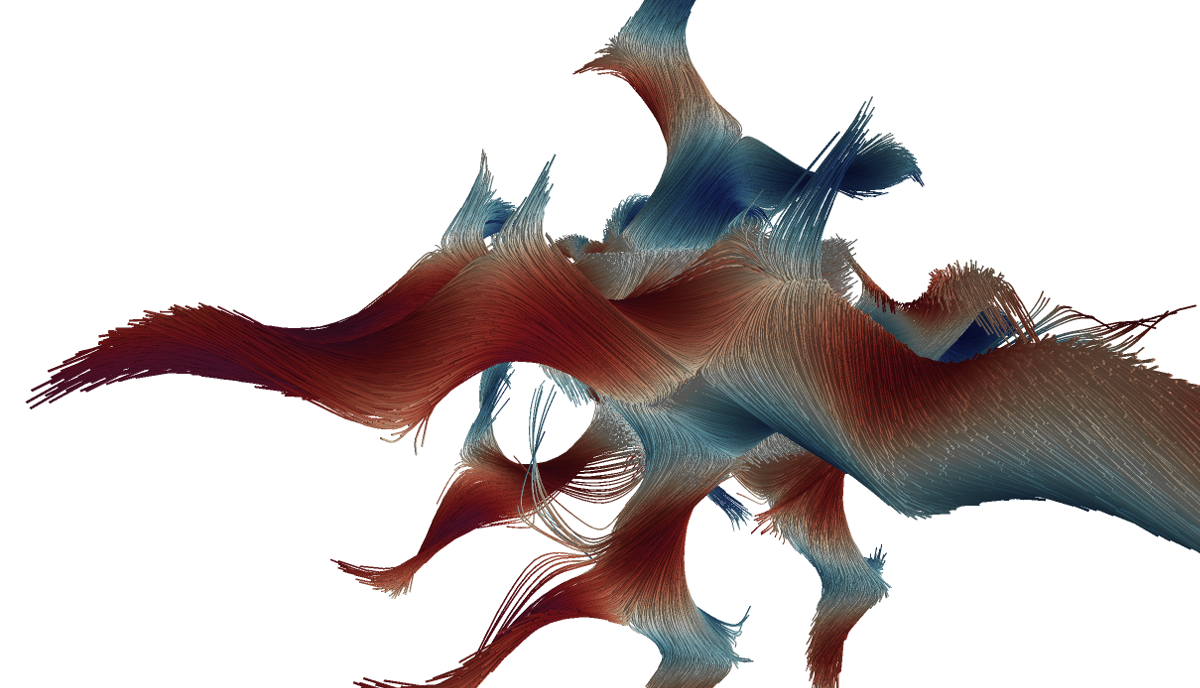
We propose a sampling technique for data reduction to reduce e.g. large cosmological simulations of dark matter (left) or trajectories of fluid flows (top right).
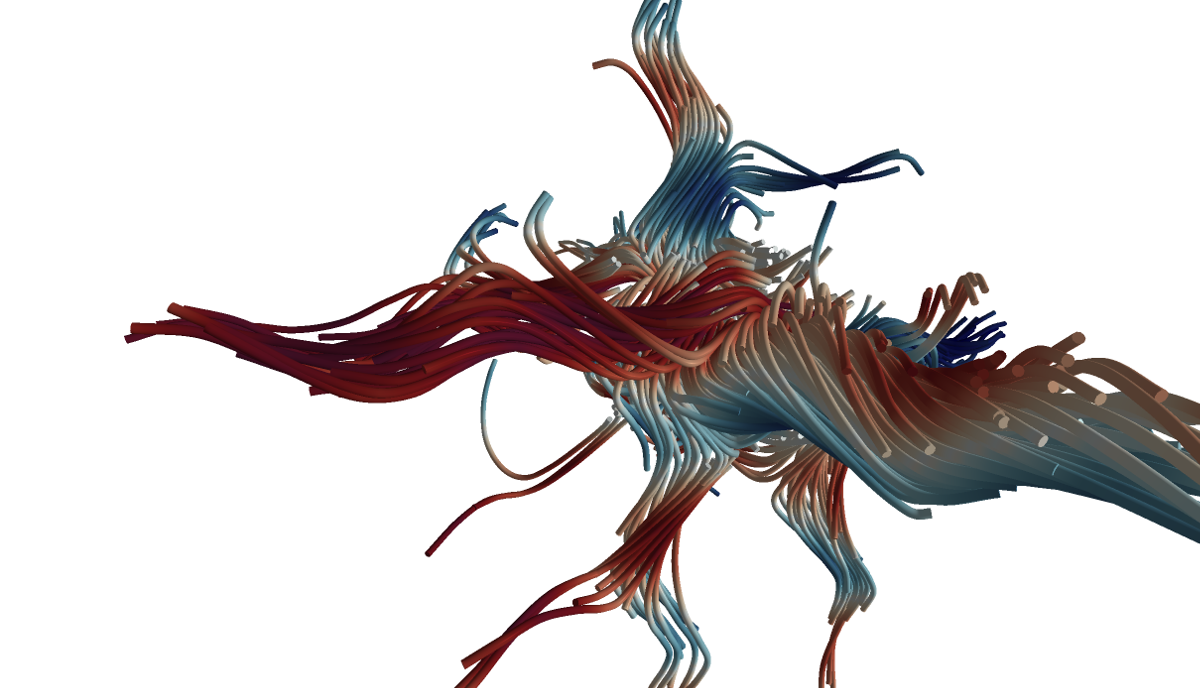
Our sampling technique implicitly provides a continuous level-of-detail representation (bottom right).
Abstract
We propose a data reduction technique for scattered data based on statistical sampling. Our void-and-cluster sampling
technique finds a representative subset that is optimally distributed in the spatial domain with respect to the blue noise property. In
addition, it can adapt to a given density function, which we use to sample regions of high complexity in the multivariate value domain
more densely. Moreover, our sampling technique implicitly defines an ordering on the samples that enables progressive data loading
and a continuous level-of-detail representation. We extend our technique to sample time-dependent trajectories, for example pathlines
in a time interval, using an efficient and iterative approach. Furthermore, we introduce a local and continuous error measure to quantify
how well a set of samples represents the original dataset. We apply this error measure during sampling to guide the number of samples
that are taken. Finally, we use this error measure and other quantities to evaluate the quality, performance, and scalability of our
algorithm.
Notes
This work will be presented at IEEE Vis 2019 in Vancouver, BC.
Downloads